
__ Ready to Power Up Your Health? Meet Folate Max (5-MTHF)—the ultimate solution to unlocking your body's full potential! __
Do you often feel like something's off with your energy or mood? Or maybe you're concerned about your body's folate levels and overall wellness? __ Folate Max is here to help you feel your best by supporting your nervous system, serum folate levels, and so much more. __
Why You Need Folate Max in Your Life! __
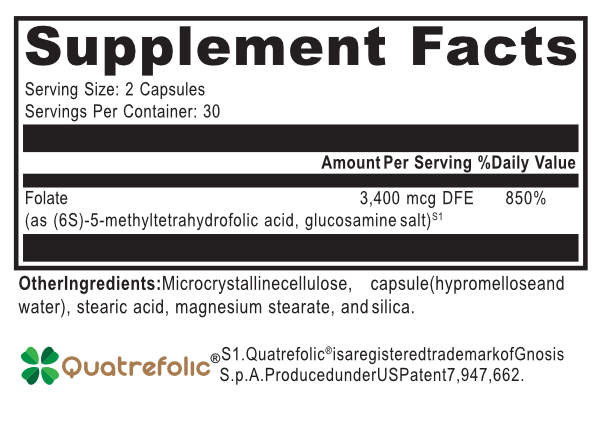
Are you one of the 20% of people with a mutated MTHFR gene? This could mean your body is struggling to convert folic acid into the active form it needs to thrive. __ Folate Max uses 5-MTHF, the most bioavailable form of folate, to give your body exactly what it needs—no more guessing or struggling with conversion! __
Here's How Folate Max Can Help You:
__ Boosts Your Energy & Mood: Methyl-folate plays a key role in creating neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, helping you stay calm, focused, and feeling good.
__ Supports Brain & Nervous System Health: Folate is essential for healthy brain function, so if you've been feeling mentally foggy, this is your answer! __
__ A Healthy Pregnancy Starts Here: Folate is vital for a healthy pregnancy outcome, and Folate Max gives you all the folate you need to support both mom and baby. ____
__ More Effective Than Regular Folate: Why settle for less when you can have Quatrefolic—a highly bioavailable form of 5-MTHF that's better absorbed and more stable than folic acid? This means you're getting the best folate in the most effective form possible! __
Ready to Feel Amazing?
_ Whether you're looking to improve your mood, boost your energy, or ensure your body is getting the folate it needs, Folate Max (5-MTHF) is the perfect addition to your daily routine!
Why settle for average when you can thrive with Folate Max? __ Grab yours today and supercharge your health! __
__ Don't wait! Click "Add to Cart" and start feeling your absolute best! __
The Healthmasters Standard
GMP Certified
Facility
Proudly Made
in the USA
Non-GMO
Certified Formula
Gluten-Free &
Soy-Free
Third-Party
Lab Tested
No Artificial
Additives
or Preservatives

